Colonial Pipeline restarts operations days after hack amid a run on gas at many stations

- Share via
CLEMMONS, N.C. — The nation’s largest fuel pipeline restarted operations Wednesday, days after it was forced to shut down by a gang of hackers.
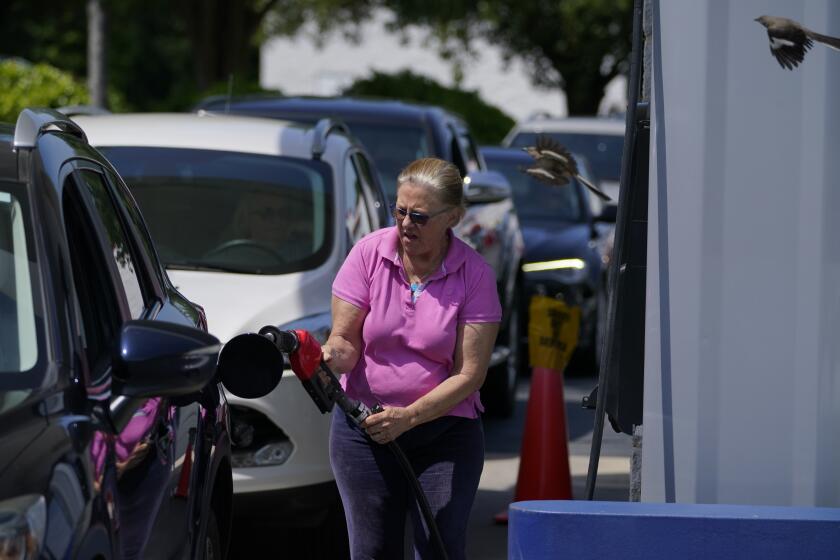
The disruption of Colonial Pipeline caused long lines at gas stations in the Southeast due to distribution problems and panic buying, draining supplies at thousands of gas stations.
Colonial initiated the restart of pipeline operations late Wednesday, saying in a statement that “all lines, including those lateral lines that have been running manually, will return to normal operations.”
But it will take several days for deliveries to return to normal, the company said.
In the meantime, drivers have been finding gas stations with little or no gas in some Southeast states.
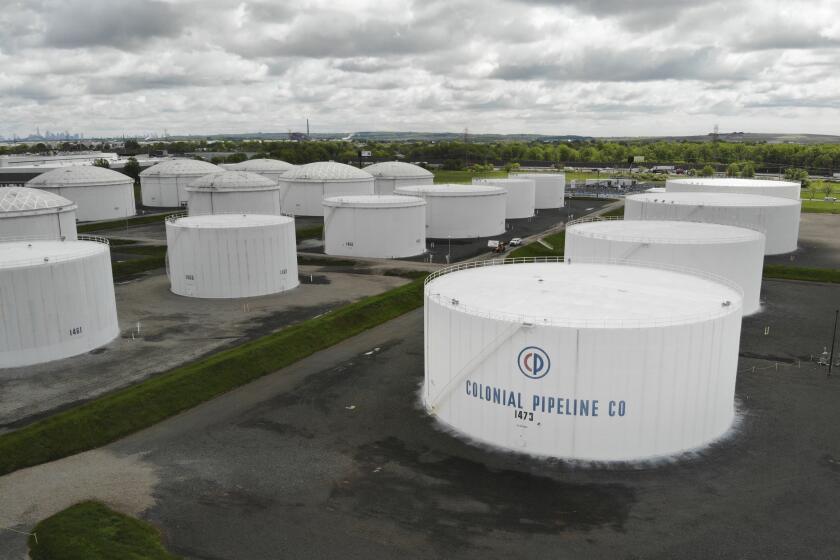
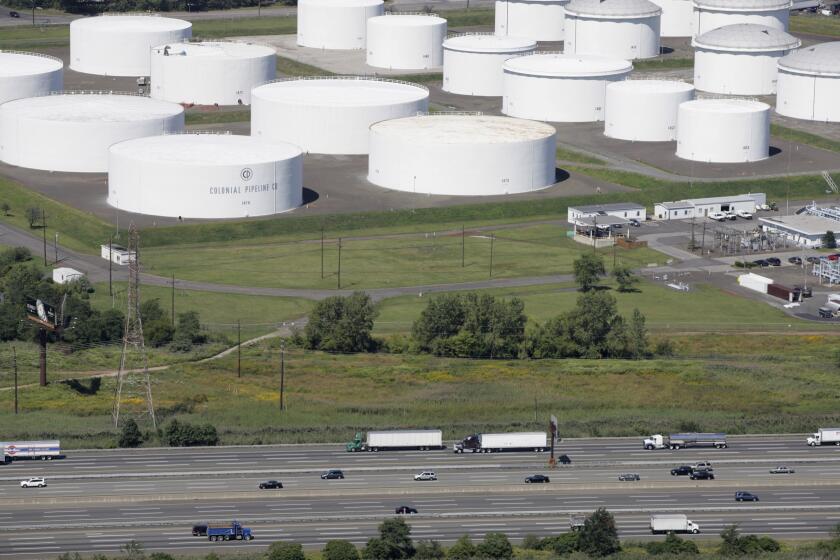
The Colonial Pipeline, which delivers about 45% of the fuel consumed on the East Coast, was hit Friday with a cyberattack by hackers who lock up computer systems and demand a ransom to release them. The hackers didn’t take control of the pipeline operations, but Colonial shut the pipeline down to contain the damage.
Hackers succeeded in shutting down a major U.S. oil pipeline. Such cyber extortion schemes are on the rise, and U.S. infrastructure remains at risk.
The attack raised concerns, once again, about the vulnerability of the nation’s critical infrastructure.
“What you’re feeling is not a lack of supply or a supply issue. What we have is a transportation issue,” said Jeanette McGee, spokeswoman for the AAA auto club. “There is ample supply to fuel the United States for the summer, but what we’re having is an issue with is getting it to those gas stations” because the pipeline is down.
The pipeline runs from the Gulf Coast to the New York metropolitan region, but states in the Southeast are more reliant on it. Other parts of the country have more sources to tap. For example, a substantial amount of fuel is delivered to states in the Northeast by massive tankers.
Jamar Gatison, 36, was filling up his tank in Norfolk, Va., Wednesday before a doctor’s appointment.
“I’m about to run out of gas, so I have no choice,” the construction worker said while waiting in line at a 7-Eleven.
“I’m also an Uber Eats driver. I also need gas for that,” said Gatison, who added that he probably won’t deliver food Wednesday night because he doesn’t want to wait in line again while the shortage continues.
Mary Goldburg, 60, of Norfolk waited more than 20 minutes for a slow-operating pump at a 7-Eleven to fill up her tank Wednesday. Her job includes delivering T-shirts for events and other promotional products.
“I can’t get paid until my customers get their products,” Goldburg said.
Gas prices are rising everywhere, even in Southern California, far from the Colonial pipeline shut down by cyberattack. California has its own issues.
In North Carolina, 65% of gas stations were out of fuel, according to Gasbuddy.com, a technology firm that tracks real-time fuel prices across the country. Just outside Raleigh, two people were charged with assault after fighting and spitting in each other’s faces while arguing over their spots in line Tuesday at a Marathon gas station, authorities said.
North Carolina Gov. Roy Cooper urged people Wednesday to buy gas only if their tank is low and to report any instances of price gouging.
“This news is another reason people do not need to panic buy gas right now unless they really need it,” he tweeted after Colonial announced it was restarting the pipeline.
Georgians were also getting squeezed, with 43% of stations there out of gas, according to Gasbuddy.com. In Virginia, 44% of stations were out, and in South Carolina, 16% had no fuel.
Along the Appalachian Trail, which stretches from Georgia to Maine through some of the most rugged and remote terrain in the Southeast, hikers depend on car and van shuttles to ferry them to and from the trail and get them back to civilization.
“If I don’t have the gas, I’m not running,” said Ron Brown of Ellijay, Ga., who operates Ron’s Appalachian Trail Shuttles and often takes hikers on hours-long trips from Atlanta’s airport into the north Georgia mountains, and to and from many points along the trail.
The shutdown of a pipeline that carries gasoline and other fuel from Texas to the Northeast is continuing.
The disruption is taking place at the time of year when Americans begin to become more mobile, especially as the nation emerges from the pandemic.
Four to five cars were lined up at each pump at a Circle K in Clemmons, N.C. Several people said they had driven to multiple gas stations to find one that had gas. Across the street, gas stations were out of fuel.
Mair Martinez, who works in landscaping, was filling up his lawn equipment and truck after checking several other gas stations without luck.
“That’s why we’ve come in today, to fill up everything,” he said.
Johnathan King, who works for a towing company, was filling up his tow truck. He said he typically does 10 to 12 service calls a day, driving between several area cities.
“It’s going to be very hard for us. Hopefully we’ll be able to get through it,” he said.
Multiple U.S. agencies coordinated to relax rules and enable fuel to be shipped faster using trucks, trains or ships, but those changes had little effect Wednesday.
The White House said the Department of Transportation is now allowing states served by the pipeline to use interstate highways to transport overweight loads of gasoline and other fuels. But there’s a national trucker shortage, so the industry isn’t able to put many more trucks on the road.
About 121,000 convenience stores nationwide sell about 5,300 gallons per day of gasoline, accounting for about 80% of retail fuel sales. At many stores demand has been two to five times the normal amount, Jeff Lenard of the National Assn. of Convenience Stores said in a conference call with reporters. Retailers were even running out of fuel in parts of Florida that are not dependent on the pipeline, he said.
Rationing has been imposed after some natural disasters, including Hurricane Sandy in 2012, but there could be resistance to that this time, especially if it looks like the pipeline could return to normal operation in a few days.
It could also backfire. “Once rationing occurs, more panic buying ensues,” said Ryan McNutt, CEO of the Society of Independent Gasoline Marketers of America.
The national average price for a gallon of gasoline ticked above $3 on Wednesday for the first time since 2016, according to the AAA, hitting $3.008. Prices begin to rise around this time every year.
“You go to some states, and you’re going to see much higher increases, especially in the South, because that’s where you’re seeing the largest impact in terms of strain of gasoline, or strain of people,” McGee said.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.