Renewed hopes, but more delays, for Cuban families seeking reunification in U.S.
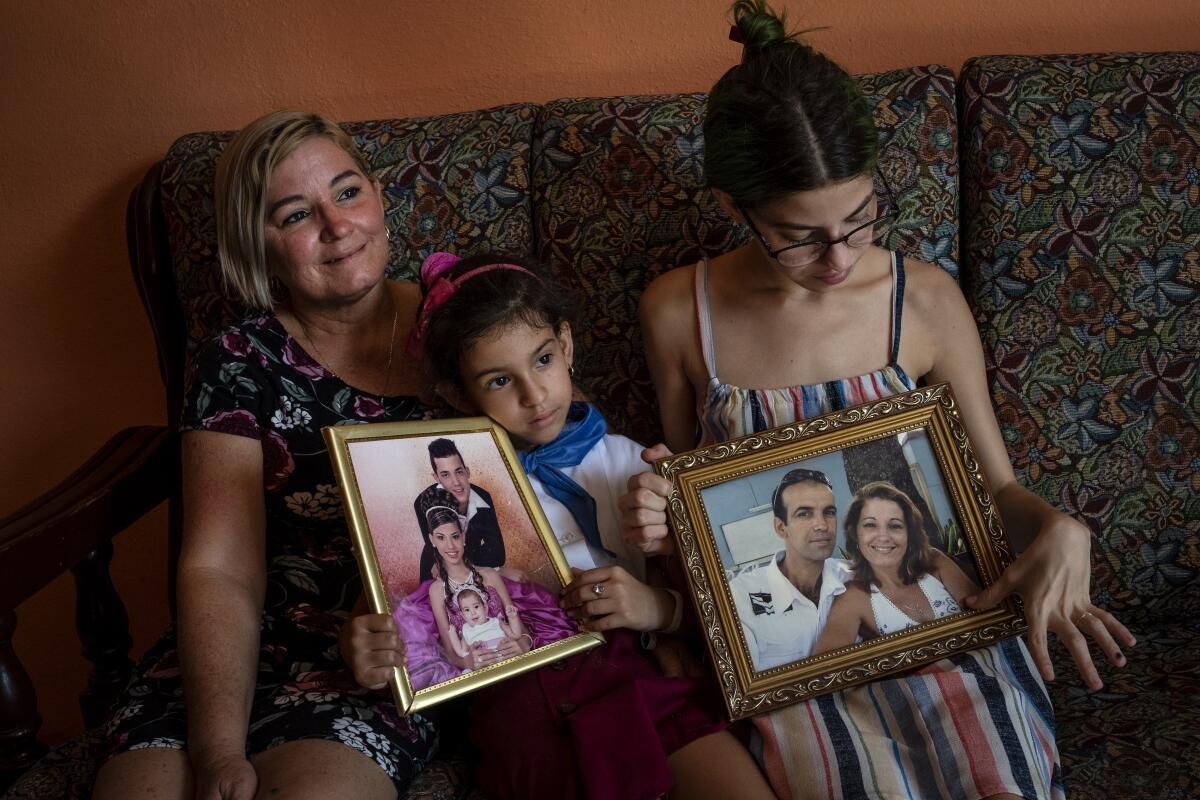
- Share via
CIENFUEGOS, Cuba — Like many Cubans before him, Roberto De la Yglesia left most of his family behind when he made his way to the United States with only his son in 2015, hoping that he could soon bring his wife and daughters to join him.
Years later, the mechanical engineer in New Jersey and his family back in Cienfuegos, Cuba, are still waiting — with a mixture of renewed hope and skepticism — now that the Biden administration has said it would reactivate the long-stalled Family Reunification Program, which allows Cubans legally in the U.S. to bring in close relatives.
“My life is on pause,” said De la Yglesia’s wife, Danmara Triana, sitting on the sofa of her house in Cienfuegos while surrounded by aging photos of the couple’s life together. A few feet away, her 21-year-old daughter Claudia was awaiting the return from school of 7-year-old Alice.
“My day-to-day life hangs on this — to see my son, to see my husband,” Triana said.
The 48-year-old accountant said she repeatedly checks the website of the U.S. Embassy in Havana for news.
“I get up in the morning and look at the telephone,” she said. “Will I have an interview [for a visa] or won’t I have an interview?”
The Biden administration says it will expand flights to Cuba and lift Trump-era restrictions on remittances that immigrants can send to people on the island
The Biden administration says that roughly 20,000 applications for family-reunification visas have built up since 2017. That’s when then-President Trump effectively shut down the program by withdrawing diplomatic personnel from Cuba in response to a spate of mysterious illnesses among diplomats that many suspected were the result of some sort of directed wave attack.
But many similar incidents happened elsewhere — even in Washington — and the CIA has now determined that they were unlikely to be the result of attacks by Russia or other foreign adversaries.
While the administration said in April it would begin resuming the visa program, it has not yet offered a timeline for ramping up the U.S. diplomatic presence in Cuba.
So Triana and De la Yglesia wait.
The decision throws the summit, which is crucial to the U.S. ability to demonstrate its influence in the western hemisphere, into further disarray.
U.S. officials told the couple in 2017, shortly before diplomats were withdrawn, that they qualified for the program, and in 2020 they believed they had finished all the paperwork and paid all the fees.
Then the COVID-19 pandemic hit, adding to complications.
“I feel stranded. I’m not based anywhere,” said Claudia, who said she had dropped out of medical school, feeling “horribly unmotivated.”
The withdrawal of diplomats was only one of many steps by the Trump administration to isolate Cuba and backtrack from a dramatic opening to the island under President Obama.
Breaking News
Get breaking news, investigations, analysis and more signature journalism from the Los Angeles Times in your inbox.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.
Trump enacted more than 200 measures, including a ban on cruise ships, limits on money sent from the U.S. to Cuba and restrictions on U.S. visitors to the island.
Biden announced that he would undo some — but far from all — of the Trump-era restrictions.
With consular operations idled in Havana, U.S. officials told Cubans to seek visas at the operations in Guyana, across the Caribbean on the South American mainland — a costly and impractical option for most.
So with Cuba’s economy in dire shape, increasing numbers have tried to reach the U.S. illegally, getting to South America or Mexico and making their perilous way to the U.S. border, adding to a record wave of immigrants seeking entry.
Despite campaign promises on Cuba, President Biden has not opened paths on the remittances and travel some say would most help islanders.
U.S. Customs and Border Patrol says it detained Cubans 79,800 times at the U.S. border in the six months from October 2021 through March 2022 — more than double the figure for the full 12 months ending in September 2021 and five times the figure for the year before that.
Next door to Triana’s house, 61-year-old Natacha González lives with her two grandchildren. Her daughter, like De la Yglesia, now lives in the U.S. and began the reunification process in 2017.
“I feel like I have no oxygen. ... I’ve spent years at this, and it’s not right that we are still waiting,” González’s daughter, Yanelis León, said in a video call from Florida. “I am not going to involve my children in a migration across borders where I am going to lose them. I want to do things right.”
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.