Now it’s BA.4: New subvariant fuels coronavirus surge in South Africa, where Omicron emerged

- Share via
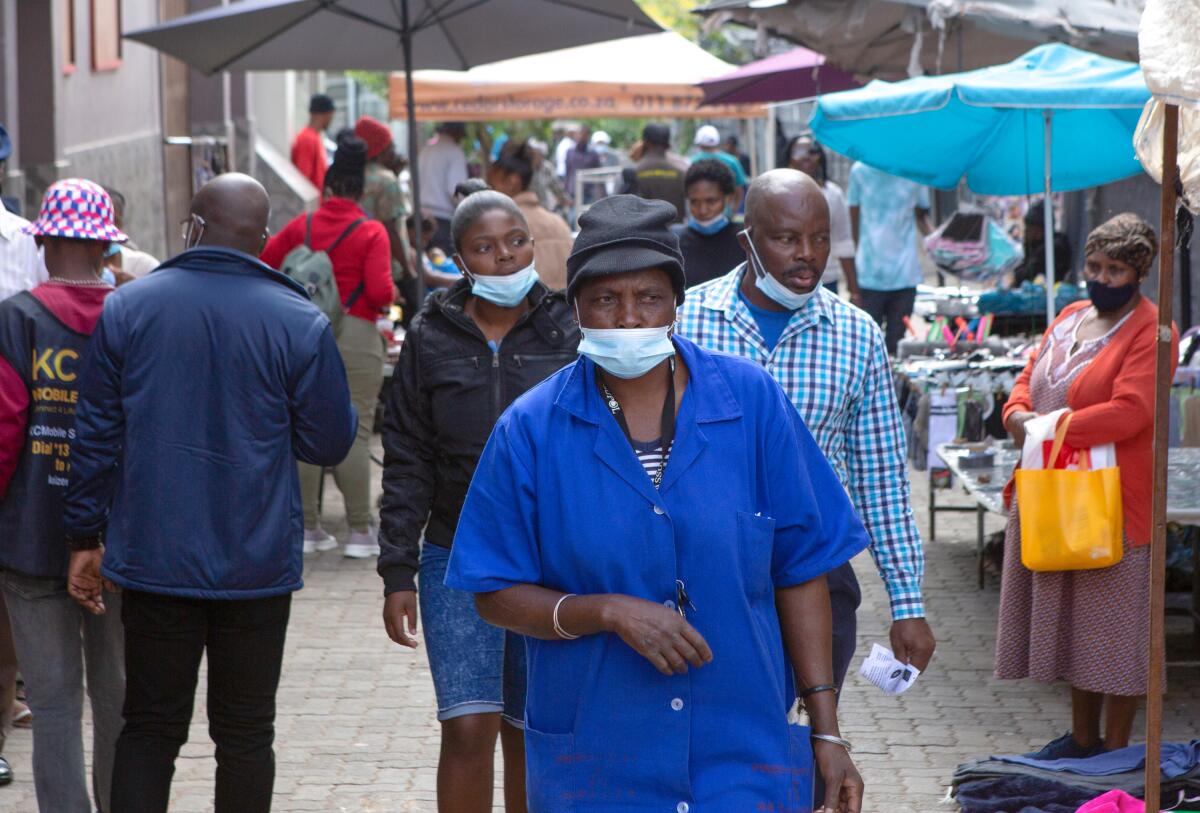
JOHANNESBURG — South Africa is seeing a rapid rise in coronavirus cases driven by yet another version of the virus, health experts say.
Cases had been dropping in the country since February. But a new Omicron subvariant that scientists call BA.4 began pushing up cases last week, and they have risen rapidly since, said Salim Abdool Karim, who previously advised the government on its COVID-19 response.
So far, there has been only a slight rise in hospitalizations and no increase in deaths, said Abdool Karim, who is a public health expert at the University of KwaZulu-Natal.
South Africa is recording more than 6,000 coronavirus cases a day, up from a few hundred just a few weeks ago. The proportion of positive tests jumped from 4% in mid-April to 19% Thursday, according to official figures. Wastewater surveillance has also shown increases in coronavirus spread.
The new mutant appears to be quickly achieving dominance over the original Omicron variant and other versions of the coronavirus, but Abdool Karim said that “it’s too early to tell whether BA.4 is going to cause a fully fledged wave.”
Still, the new version is notable because the Omicron variant first emerged in November in South Africa and Botswana before sweeping around the world.
The increase in coronavirus cases is “pretty significant,” a top official said, underscoring the importance of vaccinations, booster shots and masks.
There is one concerning trend, said Helen Rees, executive director of the Reproductive Health and HIV Institute at the University of Witwatersrand in Johannesburg: Children are the first to be winding up in hospitals, just as during the original Omicron surge.
Experts say BA.4 seems to be more transmissible than the original Omicron variant and the “stealth” subvariant known as BA.2. Scientists are still studying the new mutant, but it doesn’t appear that BA.4 causes more severe disease than other versions of the virus, the World Health Organization said in a recent report.
In South Africa, gatherings for the recent Easter, Ramadan and Passover holidays, plus massive flooding in the coastal city of Durban, may have contributed to the current surge, Abdool Karim said.
BA.4 has shown up in other countries, but it’s not clear whether “it’s going to become a globally dominant variant,” he said.
What accounts for BA.2’s recent success? It’s not due to an ability to evade the protection of COVID-19 vaccines, a new study finds.
So far, it hasn’t made inroads in the U.S., where BA.2 remains the dominant strain and its descendant, called BA.2.12.1, is gaining ground. That descendant is believed to spread faster than previous versions of the virus and caused about 29% of U.S. coronavirus cases in the latest week, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Can BA.4 out-compete BA.2.12.1? Dr. Stuart Campbell Ray, a Johns Hopkins University infectious disease expert, said the two variants are spreading in different populations, and he doesn’t know of any data “that would support a robust direct comparison.”
Since the start of the pandemic, South Africa has had the lion’s share of COVID-19 cases in Africa. Although the country’s 60 million people account for less than 5% of Africa’s population of 1.3 billion, South Africa has had more than one-quarter of the continent’s 11.4 million reported cases and nearly half of Africa’s 252,000 deaths.
Experts say that may be because it has a more developed public health system and keeps better records of hospitalizations and deaths than other African countries.
‘Deltacron’ is a hybrid of Delta and Omicron. How worried should California be?
More than 44% of adult South Africans are vaccinated against COVID-19, according to government statistics.
Benido Impouma, a WHO official in Africa, said the latest surge “shows that people must remain vigilant and continue to adhere to public safety measures such as wearing masks, washing hands and social distancing.”
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.