Coronavirus can destroy the placenta and lead to stillbirths
- Share via
New research suggests the coronavirus can invade and destroy the placenta and lead to stillbirths in infected women.
It’s an uncommon outcome for any pregnancy, but women with COVID-19 face an elevated risk. Authorities believe vaccination can help prevent these cases.
Researchers in 12 countries, including the United States, analyzed placental and autopsy tissue from 64 stillbirths and four newborns who died shortly after birth. The cases all involved unvaccinated women who had COVID-19 during their pregnancy.
The study bolsters evidence from small case reports and confirms that placenta damage — rather than an infection of the fetus — is the likely cause of many COVID-19-related stillbirths, said Dr. Jeffery Goldstein, a pathologist at Northwestern University’s Feinberg School of Medicine.
He was not involved in the study, which was published Thursday in Archives of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine.
Previous evidence suggests the chances of stillbirth are higher than usual for pregnant women with COVID-19, particularly if infected with the Delta variant. Vaccination recommendations include pregnant women and note their higher risk for complications when infected.
Dr. David Schwartz, an Atlanta pathologist who led the study, said other infections can infiltrate the placenta and cause stillbirth, typically by infecting and damaging the fetus. A recent example is the Zika virus.
Pregnant women with COVID-19 face a significantly higher risk of death and of complications for themselves or their newborns, a new study finds.
Schwartz and his colleagues wanted to see if that was the case with stillbirths in women with COVID-19. But what they found was almost the opposite: It was the placenta that was infected and extensively destroyed.
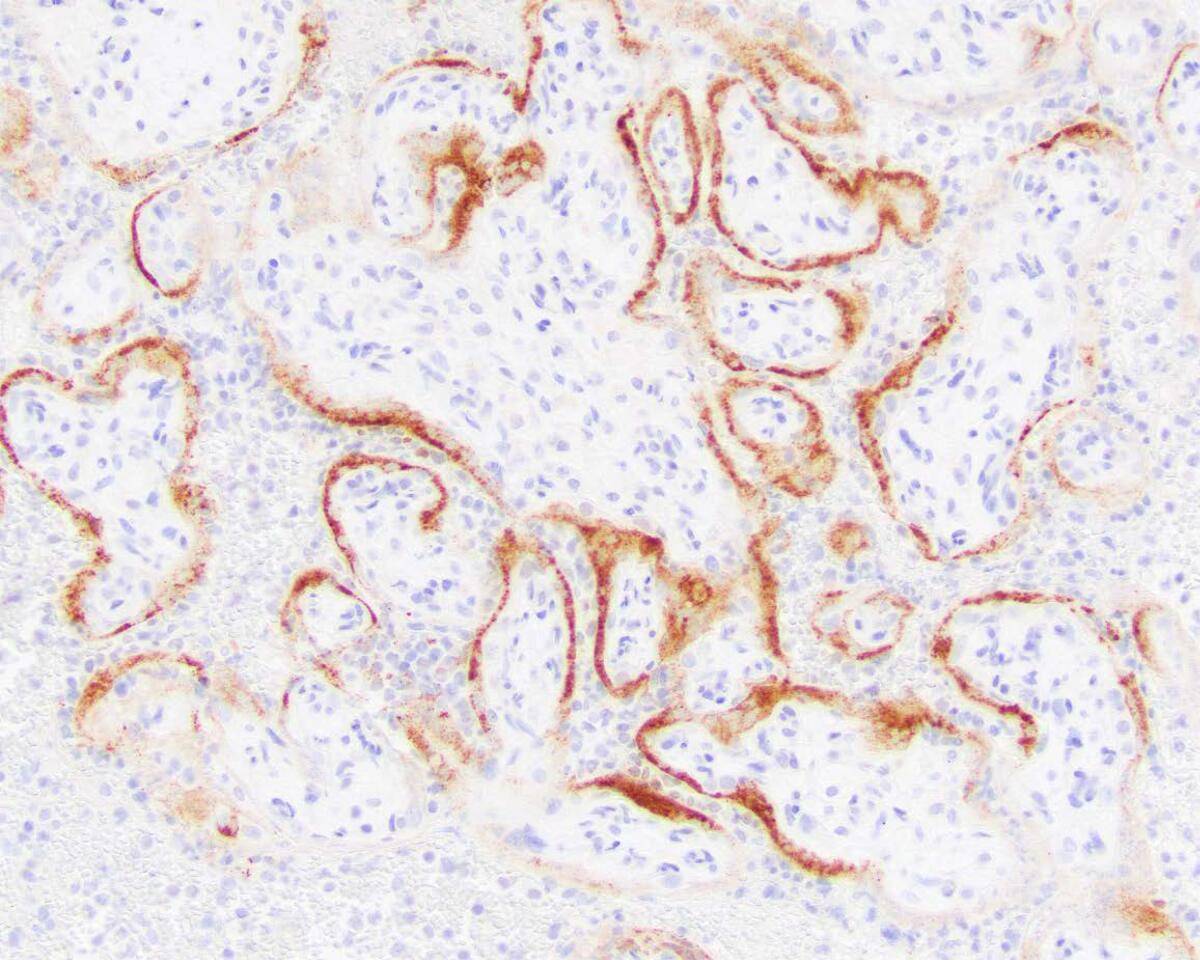
“Many of these cases had over 90% of the placenta destroyed — very scary,” said Schwartz.
Normal placenta tissue is a healthy reddish hue and spongy. The specimens they studied were stiff, with dark discolorations of dead tissue. While other infections can sometimes damage the placenta, Schwartz said he’d never seen them cause such consistent, extensive destruction.
The placenta is an organ that forms and attaches to the womb during pregnancy. It connects with the umbilical cord, providing oxygen and nourishment from the mother’s bloodstream.
The virus likely reached the placenta through the bloodstream, attaching to susceptible cells and causing protein deposits and an unusual form of inflammation that blocked blood flow and oxygen. That in turn led to placenta tissue death and suffocation, the researchers said.
A long-standing tradition of keeping pregnant women out of clinical trials is having serious consequences with regard to COVID-19.
Coronavirus was also detected in some of the fetuses, but evidence of suffocation in the womb points to placenta damage as the more likely cause of death, they said.
A Centers for Disease Control and Prevention report in November found that among pregnant U.S. women infected with COVID-19, about 1 in 80 deliveries was a stillbirth — the loss of a fetus anytime after 20 weeks. That’s compared with 1 in 155 among uninfected women.
The stillbirths in the study occurred on average at 30 weeks; normal pregnancies last about 40 weeks.
High blood pressure, certain chronic illnesses and fetal abnormalities are among conditions that can increase chances for stillbirths, including in women with COVID-19.
It is unclear whether Omicron infections also increase chances for stillbirths; the study was done before the highly infectious variant emerged.