Alzheimer’s drug stirs hope for patients, worry for doctors

- Share via
In the weeks since a new Alzheimer’s drug was approved, hopeful patients have bombarded Dr. Alireza Atri with calls and emails about a treatment that has sparked both excitement and skepticism.
They want to know if the drug might be right for them. Like many physicians, Atri has no easy answers.
“It’s not a simple yes or no,” said the neurologist at the Banner Sun Health Research Institute in Arizona.
It probably won’t be for a while. Doctors across the country are still trying to figure out who should receive the drug called Aduhelm, which, at best, slows the fatal disease marginally. Other drugs for Alzheimer’s disease only temporarily ease symptoms such as memory problems, insomnia and depression.
Although some clinics have already started giving the drug, many providers say it will take weeks or months before they are ready. Insurers — including the biggest bill payer for this drug, Medicare — still need to determine which patients to cover for a treatment that could cost more than $50,000 a year. And doctors worry that emotions will affect decisions by patients and families in seeking the drug.
“People are desperate. It’s a really horrible disease,” said Stanford University’s Dr. Michael Greicius.
U.S. regulators have OKd the first new Alzheimer’s drug in nearly 20 years, against the advice of their own outside experts.
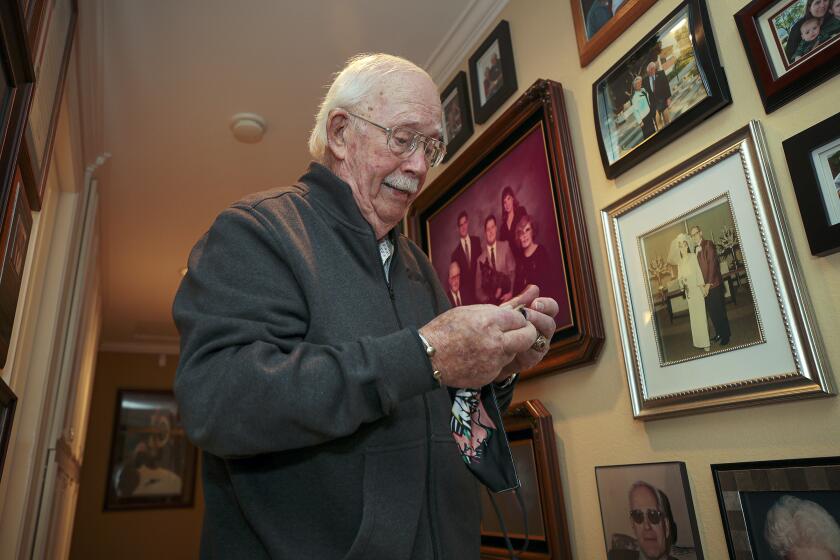
Karl Newkirk hopes to start taking Aduhelm if his doctor gives the OK because he doesn’t see any other treatments worth trying.
“It looks like the only star in the sky,” said the 80-year-old Sarasota, Fla., resident, who has early-stage Alzheimer’s.
Newkirk’s doctor confirms he’s a good candidate for the drug. Although the retired technology consultant is still fit enough to ride roller coasters with his grandchildren at nearby Busch Gardens, he struggles with short-term memory loss. He wants to try Aduhelm, even though he’s aware of the drug’s limits.
Michele Hall, 54, of Bradenton, Fla., also is eager to discuss the drug at her next appointment with an Alzheimer’s specialist.
A former government attorney, Hall had to quit her job after struggling with once-simple tasks including spelling, public speaking and remembering deadlines. She was diagnosed with early Alzheimer’s in November by doctors at the Mayo Clinic.
Hall calls Aduhelm “the first tiny glimmer of hope” that she has had that she might get more quality time with her husband and their three adult children.
“When you get that diagnosis, you really wake up every morning and go, ‘Here I am, it’s ticking away, and I’m just waiting,’” she said. “Well, now you have something to look forward to.”
Biogen’s Aduhelm is the first Alzheimer’s medication in nearly 20 years. Its Food and Drug Administration approval earlier this month triggered a swift backlash from many experts, including the agency’s own outside advisors, who had warned that its supposed benefit relied on flimsy data. Three resigned over the FDA’s decision.
Aduhelm does not reverse mental decline. It only slowed it in one study that was marred by hard-to-interpret results. The data were so murky that the FDA ultimately granted the drug conditional approval based on a different measure: its ability to get rid of harmful clumps of plaque in the brains of patients with early forms of the disease.
How did the FDA got browbeaten into approving an Alzheimer’s drug that may not work?
The FDA approval isn’t limited to those early patients. Anyone with Alzheimer’s — at least theoretically — could be prescribed the drug. But advocacy groups such as the Alzheimer’s Assn. and many doctors say the focus should be on patients with an early diagnosis, like those helped in the study.
“I don’t want to see people pull their mothers from nursing homes to get this treatment,” said Dr. Babak Tousi, a Cleveland Clinic geriatrician who consulted with Biogen and helped run one of the testing sites for Aduhelm.
Safety will be a key consideration, according to Dr. Ronald Petersen at the Mayo Clinic, which is coming up with its own use guidelines for the drug.
“We want to be conservative here,” said Petersen, an Alzheimer’s specialist who has consulted with most major drugmakers in the field, including Biogen.
About 40% of patients getting the full drug dose in Biogen’s studies had swelling or tiny bleeds in the brain. Although the side effects usually resolved, in rare cases they led to more severe bleeding that could potentially cause brain injury or other dangerous complications.
Monitoring patients on the drug involves regular brain scans. That’s on top of a different type of scan to tell if patients have the brain plaque targeted by the drug. Running all those tests could easily approach $10,000 the first year, according to physicians.
Insurers will likely require prior approval of those scans, which could delay care. And, depending on coverage, patients still might be liable for thousands of dollars annually from the scans and treatments due to deductibles and other out-of-pocket costs.
The FDA’s approval of an Alzheimer’s drug of dubious value will throw U.S. healthcare spending into crisis.
Biogen says about 900 sites in the U.S. have the equipment and expertise to immediately begin giving the drug, which requires monthly IVs.
The private Michigan Institute for Neurological Disorders has already started treating early-stage Alzheimer’s patients. The institute said it would pick up most of the cost if an insurer ultimately denied coverage “because it’s a therapy we believe in,” a spokeswoman said.
Meanwhile, Stanford’s Greicius, a neurologist and Alzheimer’s specialist, has no plans to prescribe Aduhelm.
“I don’t think there’s sufficient evidence that it works, and there’s plenty of evidence that it can harm patients,” he said.
He said he planned to lay out a “compelling and compassionate” case for why he didn’t want to give patients the medicine. But he worries that some patients may simply turn to a doctor who will provide it.
Almost a year has passed since Gordan and Diane Norman last saw each other in person — separated by Alzheimer’s and the COVID-19 pandemic.
The Cleveland Clinic’s Tousi said talking about expectations, cost and the side effects might counter some emotional pressure to give the drug to patients not suited for it.
But part of the challenge is family members often think a patient is in an earlier stage of the disease than they actually are. He said they had to understand that the medication would not bring someone back to who they were.
“What we wish cannot always be translated to real life,” he said.
One likely consequence of Aduhelm’s approval is earlier screening and diagnosis for Alzheimer’s, a longtime aim of those who study the disease, given that it develops slowly over years or decades.
But an earlier diagnosis combined with Aduhelm’s incremental benefit may simply prolong the hardships of caring for someone with Alzheimer’s.
“It could turn out that it actually increases your caregiver burden if it’s just slowing things down a little bit,” said Dr. Suzanne Schindler of Washington University in St. Louis. “I think it’s going to be really disappointing for a lot of people.”