Supreme Court rules for coach whose prayers on field raised church-state questions
- Share via
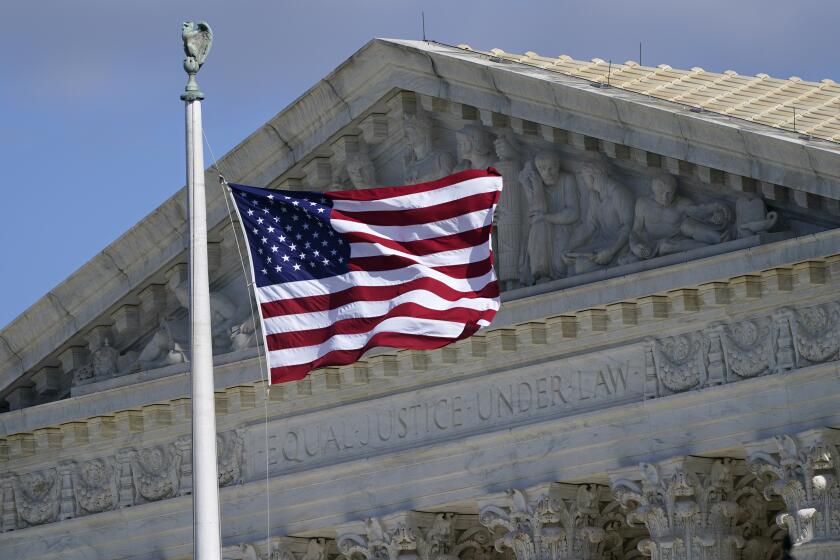
WASHINGTON — The Supreme Court on Monday sided with a former high school football coach who prayed at the 50-yard line after games, ruling that his public prayers were protected as free speech and free exercise of religion.
The 6-3 decision is a victory for those who seek a larger role for prayer and religion in public schools.
The court’s conservatives cast aside long-standing ideas that the Constitution mandates a strict separation of church and state. While they agreed students may not be required to pray or listen to a religious message, they said private prayers at school are protected, not prohibited.
They ruled that Coach Joe Kennedy’s prayers began as a personal expression, and were not official acts of promoting religion simply because they drew a crowd.
The 1st Amendment protects the freedom of speech and the free exercise of religion while prohibiting an “establishment of religion,” and all three clauses were at issue in the case of Kennedy vs. Bremerton School District.
“Both the Free Exercise and Free Speech Clauses of the 1st Amendment protect expressions like Mr. Kennedy’s. Nor does a proper understanding of the Amendment’s Establishment Clause require the government to single out private religious speech for special disfavor,” wrote Justice Neil M. Gorsuch for the court. “The Constitution and the best of our traditions counsel mutual respect and tolerance, not censorship and suppression, for religious and nonreligious views alike.”
The court’s three liberals dissented.
“This case is about whether a public school must permit a school official to kneel, bow his head, and say a prayer at the center of a school event. The Constitution does not authorize, let alone require, public schools to embrace this conduct,” said Justice Sonia Sotomayor.
Since 1962, “this court consistently has recognized that school officials leading prayer is constitutionally impermissible. Official-led prayer strikes at the core of our constitutional protections for the religious liberty of students and their parents, as embodied in both the Establishment Clause and the Free Exercise Clause of the 1st Amendment,” Sotomayor said.
The ruling drew sharply contrasting reactions.
“This is a tremendous victory for Coach Kennedy and religious liberty for all Americans,” said Kelly Shackelford, president of the Texas-based First Liberty Institute, which represented the coach. “Our Constitution protects the right of every American to engage in private religious expression, including praying in public, without fear of getting fired.”
Rachel Laser, president of Americans United for Separation of Church and State, said the “decision represents the greatest loss of religious freedom in our country in generations. This court focused only on the demands of far-right Christian extremists, robbing everyone else of their religious freedom. It ignored the religious freedom of students and families.”
Kennedy was an assistant coach on a yearly contract at Bremerton High School in Washington state when he began to pray at the end of games. School officials warned him against continuing the prayers because they had become a public event. They said his prayers at schools could be seen as violating the Constitution’s ban on an “establishment of religion.”
Kennedy said he would fight the decision and took his case to the local media. He was suspended when he refused to follow the district’s guidance, and he was not rehired for the next year. He then sued the district for firing him in violation of his constitutional rights.
He lost before a federal judge and the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals. Its judges agreed with the school district that allowing his public prayers could violate the ban on an establishment of religion.
“Kennedy spoke as a public employee when he kneeled and prayed on the 50-yard line immediately after games while in view of students and parents,” said Judge Milan Smith for the 9th Circuit. His opinion said schools may regulate or restrict what public employees say on the job, even while they are free to speak as they wish on their own time.
The high court said the key issue was whether the coach’s prayers were private and personal, or whether they were the public acts of a government employee.
“It seems clear to us that Mr. Kennedy has demonstrated that his speech was private speech, not government speech,” Gorsuch wrote. “When Mr. Kennedy uttered the three prayers that resulted in his suspension, he was not engaged in speech ordinarily within the scope of his duties as a coach. He did not speak pursuant to government policy. He was not seeking to convey a government-created message. Simply put: Mr. Kennedy’s prayers did not “ow[e their] existence” to Mr. Kennedy’s responsibilities as a public employee.”
In the past, the court had ruled that government employees are not as protected as whistleblowers if they speak or reveal confidential matters that were part of their job. But Monday’s opinion said the coach was not acting as a government employee when he prayed on the field.
Gorsuch rejected past opinions that said schools violate the Constitution whenever they appear to “endorse” religion.
“Such a rule would be a sure sign that our Establishment Clause jurisprudence had gone off the rails,” he wrote. “In the name of protecting religious liberty, the district would have us suppress it.” Adopting such a rule could require schools to “fire teachers for praying quietly over their lunch, for wearing a yarmulke to school, or for offering a midday prayer during a break before practice,” he said.
Notre Dame law professor Richard Garnett praised the court’s opinion and said it will clarify the law.
“The Establishment Clause is concerned with the entanglement of governmental and religious authority,” he said. “It does not require the censorship of private religious expression.”
Daniel Mach, an ACLU lawyer, called the decision a setback for religious liberty.
“It’s inherently coercive for school officials to pray with students while on duty,” he said. “Today’s ruling ignores that basic principle, and tramples the religious freedom of students who may not share the preferred faith of their coaches and teachers.”
Last week, the court ruled for parents in Maine who sought state tuition aid to send their children to a religious school. Because the state subsidized tuition at other private schools, it could not exclude those that are religious, the court said.
In both rulings, the court’s six conservatives were in the majority and the three liberals in dissent.
More to Read
Get the L.A. Times Politics newsletter
Deeply reported insights into legislation, politics and policy from Sacramento, Washington and beyond. In your inbox three times per week.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.











