Op-Ed: Haiti before and after Moise

In trying to understand the assassination of President Jovenel Moise, Iāve been pondering its roots in recent Haitian political history.
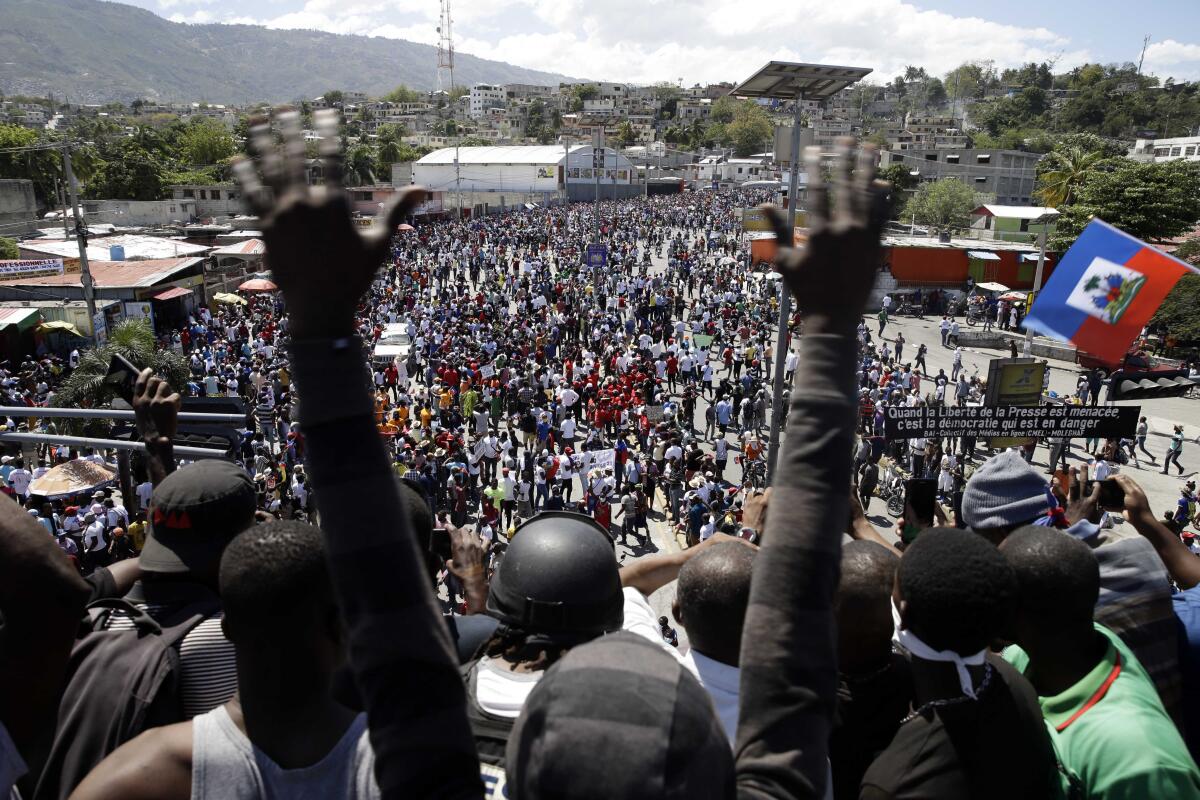
Haiti is divided into two factions: the Haitian people, who need everything, and the elite or business class, who have everything. It is basically that stark. And thatās what is being fought over as Haitians and the international community decide how to proceed with governance after Moiseās killing.
In the three decades Iāve reported on Haiti, Iāve seen two foreign occupations. One in 1994, when the Americans went in to return President Jean-Bertrand Aristide to office after heād been deposed in a coup in 1991, and another that began in 2004, when Aristide was once again ousted from the presidency. That coup led to the United Nations mission to stabilize Haiti, which remained in the country for 13 years.
In many ways, the arguments and discord today in Haiti circle back to those two foreign occupations and the reasons they were put into place.
Today, Haitiās youthful population might not even recognize Aristide, but his name is still synonymous in Haiti with the struggle of the people for representation in government and for a better life. The platform he ran on was to give all Haitians what he called āa seat at the table.ā
Those words still resonate, as a team of U.S. officials arrived in Haiti on Sunday to help with the investigation of Moiseās assassination. On Monday, the team met with three Haitian officials ā acting Prime Minister Claude Joseph, Prime Minister-Designate Ariel Henry and Senate President Joseph Lambert ā who are all vying to grab presidential authority. But none of them are constitutionally acceptable or associated with popular movements.
In the years after Aristide, the U.N., U.S., and the Organization of American States had undue influence on Haitian elections. After the 2010 earthquake, they supported ā largely behind the scenes ā a self-declared Duvalierist, Michel Martelly, in a controversial and irregular election, and then Moise, Martellyās chosen successor.
Both Martelly and Moise were elected while the U.N. was still patrolling the pro-Aristide neighborhoods of the capital, keeping the peace by firing rounds into the tin-and-cardboard shantytown houses where so many Haitian voters reside.
The right-wing, anti-democratic faction was able to triumph again ā not in coups but in elections, with the help of the U.N. occupation and the rest of the international community.
The fact is, the Haitian people are not a population the international community feels competent to deal with, whereas political figures like Martelly and Moise, who claimed to be in charge and able to run the country, are familiar and acceptable.
Both men seemed comfortable with Haitiās rising business class ā often called āthe mafiaā by Haitians. This mafia is on good terms with the international community. This mafia speaks perfect English. They have nice houses and invite diplomats to dinner. They have servants and armored cars and working generators so that they donāt have to suffer when the blackouts come. They can talk a very good game.
But did Martelly and Moise run the country properly? No.
Both men were found by a Haitian appeals court report to have participated in siphoning funds from a $2-billion petroleum discount account set up by Venezuela to benefit Haitian social programs. And thatās only one of the many corrupt schemes they and their close associates have been accused of, to say nothing of undermining Haitiās institutions, including the Legislature, the municipal bureaucracies and the courts, and allowing gangs to take control of Haitiās streets and kidnap, rob and kill innocent civilians.
Whatās most disturbing is that the support the OAS, the U.S. and U.N. have given Martelly and Moise seems to have blinded them to other actors on the Haitian scene. There are, after all, plenty of well-spoken progressives who want to help their countrymen have a better life, with free education, as well as healthcare, sanitation, COVID-19 vaccines (by the time of his death Moiseās government had offered zero vaccines to the people), retirement pensions ā and security in the streets. These were among the goals of the Aristide governments. They are still what Haitians hope for.
If the international community insists on supporting Martelly-Moise men such as Claude Joseph, whom Moise had fired as prime minister just days before his murder, there will be no free and fair elections, and the future will continue to be dark and dysfunctional for the Haitian people.
As Fulton Armstrong, a former intelligence agent who worked in Haiti for many years, told La Tercera recently: āWe have to be clear and acknowledge that the low-level agents who did the coup didnāt do it on their own initiative. Powerful forces were behind the assassination. The beneficiaries of the death of Moise are, if history is any guide, everyone except the fallen president. His assassination will provoke a feast.ā
That feast is coming soon, if the international community fails to use its powerful influence to effect real change. And everyday Haitians will not be at the table.
Amy Wilentz is the author of āThe Rainy Season: Haiti Since Duvalierā and āFarewell, Fred Voodoo: A Letter From Haiti,ā among other books.
More to Read
A cure for the common opinion
Get thought-provoking perspectives with our weekly newsletter.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.