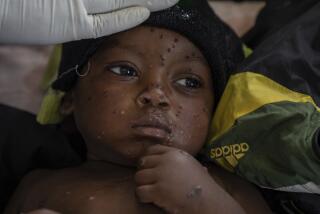
With monkeypox, San Diego’s LGBTQ community puts decades-old lessons to work
- Share via
SAN DIEGO — Four decades after a very different health crisis put a spotlight on the gay community, some San Diegans feel as though they’ve been time-warped back to the 1980s. They’re also calling on the support networks they have built since.
“Monkeypox has certainly transported me back to a time where I was scared for my life — not only because of AIDS, but because of the stigmas that came with it,” said Craig Bertrand.
Forty years ago, Bertrand was only 23 when his partner died of AIDS, just one year after the disease had been labeled a “gay-related immune deficiency.”
The monkeypox virus is very different from HIV: It is transmitted by physical contact, not sex. It is rarely fatal, unlike AIDS in its early days. And there is a vaccine to protect against it.
Get our essential investigative journalism
Sign up for the weekly Watchdog newsletter for investigations, data journalism and more.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.
But with monkeypox spreading so far mostly among gay and bisexual men, the fears and stigmas associated with it have echoed the early days of the HIV/AIDS epidemic. And for many who survived that crisis, the key differences between the viruses have made the public-health missteps this time all the more disappointing.
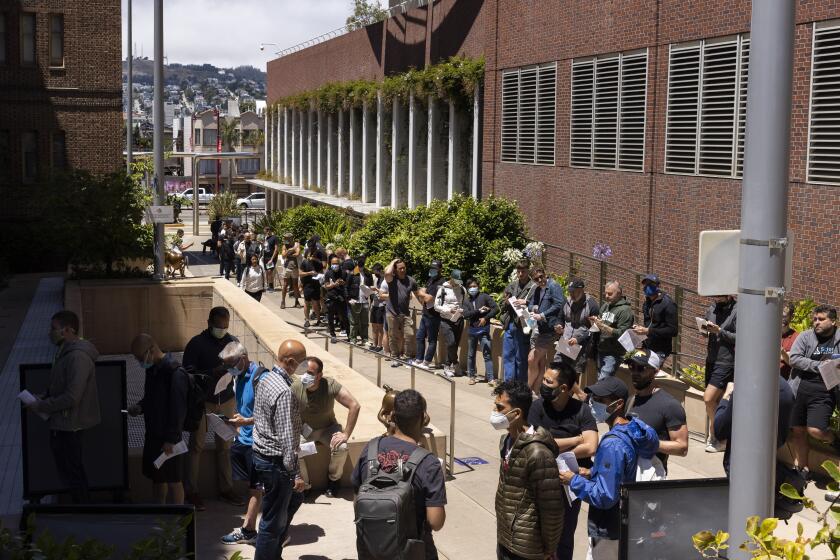
Last month, county health officials announced they’d be prioritizing the monkeypox vaccine for gay and bisexual men and for transgender people just days before Pride, renewing frustrations among local LGBTQ leaders cognizant of the stigmas their communities can face from such messaging.
In the month since, more than 100 confirmed or probable cases of monkeypox have been reported in San Diego County, bringing the total to at least 134 as of Friday, most of them among gay and bisexual men, according to county health data. The state has declared a state of emergency over the outbreak, as have the county and the nation.

Some people like Bertrand who experienced first-hand the hate and ostracization that followed the AIDS outbreak feel as though they’re reliving some of those traumas now.
“We already paid the price 40 years ago — I lost the love of my life — and now this virus has just reopened all those old wounds,” he said. “I never thought I’d be scared to consider myself a proudly gay man again, but here we are.”
Worse, he said, the health crisis comes as many are still recovering from the fear and isolation sparked by the COVID-19 pandemic — and by the growing threat of anti-LGBTQ policy around the country.
“We are already seeing the same tired hate speech targeting the LGBT community,” said Fernando Lopez, executive director of San Diego Pride. “We’ve heard all of these things before, yet here we are, fighting against going backward.”
We must educate ourselves and each other with compassion. We must stop stigma in its tracks.
Lessons learned, and not learned
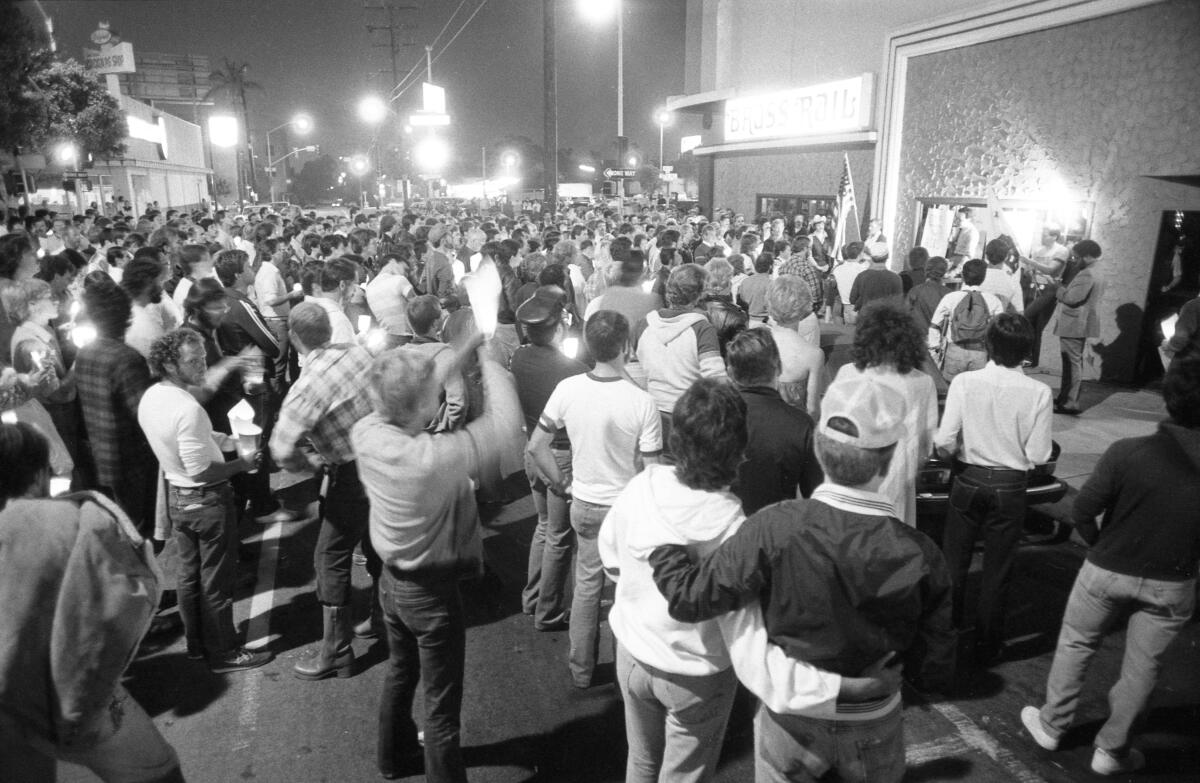
Longtime gay rights activist Nicole Murray-Ramirez recalls leading early protests during the AIDS crisis in San Diego, demanding more government help.
In one, activists marched to City Hall and placed some 200 black crosses on the step, each a memorial to someone who had died here from the disease.
“We had to fight for ourselves,” Murray-Ramirez said.
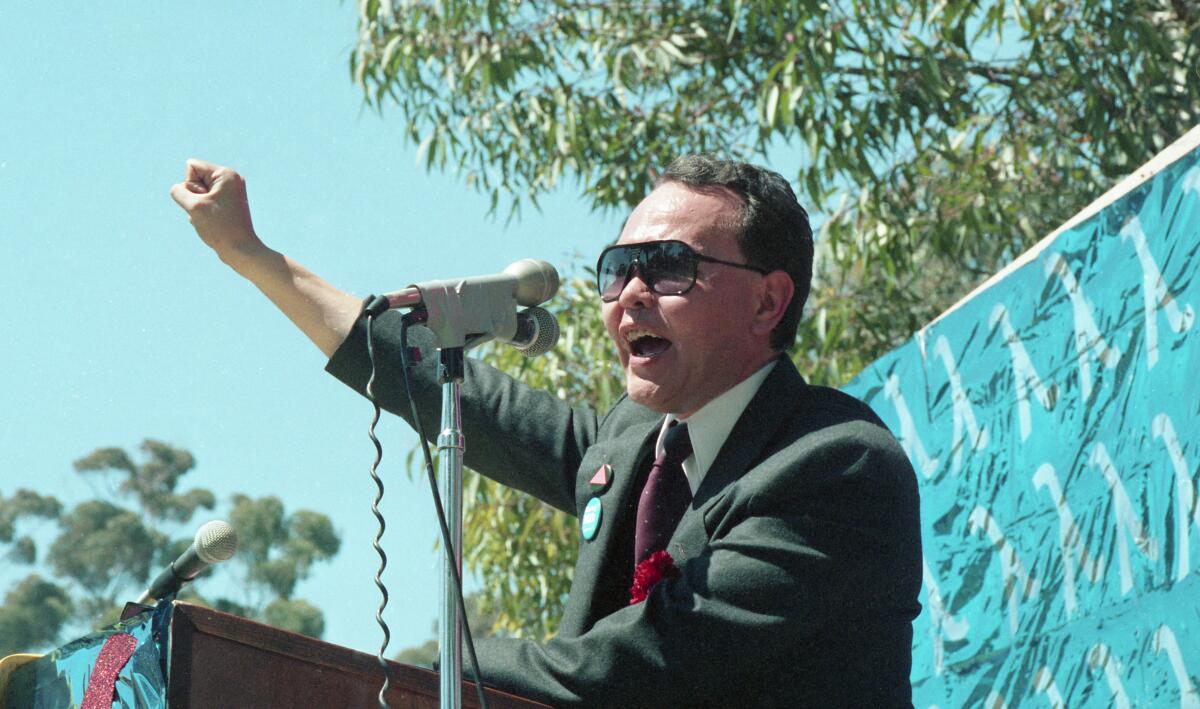

For all the world has learned since the AIDS epidemic, Murray-Ramirez believes local officials still missed early opportunities to intervene with monkeypox — such as by engaging with the most vulnerable populations in the places where they gather, for example, or making bilingual information more readily available.
“It’s kind of stunning for me and others involved in the early, dark days of AIDS that we didn’t learn more from that,” he said. “I don’t think people saw the urgency of this one [monkeypox], or understood it.”
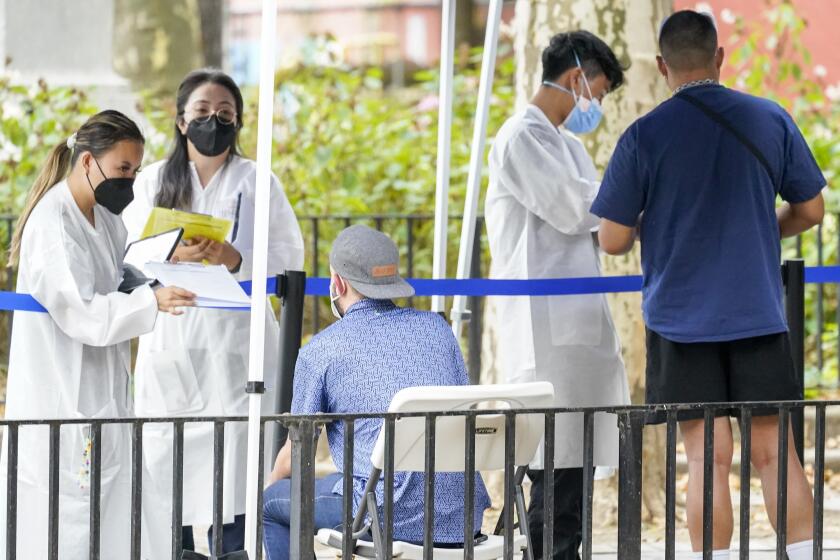
Eddie Reynoso, executive director of the Equality Business Alliance, a chamber of commerce for the LGBTQ community, agreed. Health officials at all levels were slow to react, he said — slow to engage with organizations that work with the community most directly affected by it, slow to make vaccines and testing available, slow to educate the public. “In a public health crisis, every day that goes by there are more infections,” he said.
We must put into practice what we have learned to help us fight monkeypox stigma and misinformation.
Both Reynoso and Murray-Ramirez say they have heard officials suggest that some of the hesitancy in messaging from officials came from a fear of stigmatizing the gay community.
That inadequate, “hushed” messaging by officials has only worsened the stigma by fueling speculation, said Dr. Davey Smith, chief of infectious diseases at UC San Diego Health and an HIV/AIDS specialist.
“Nobody wants to say the word ‘gay,’ afraid that it’s going to stigmatize,” Smith said. “When we talk about monkeypox, we don’t need to put it in the closet. We need to talk about it openly and honestly.”
For some health providers and advocates, it’s hard not to think about what might have been if monkeypox had been handled differently at the outset.
“If we had really strong messaging early about risk and offered the vaccine early at the sites where people are at highest risk, we probably would have been a little bit more successful,” said Dr. Chris Gordon, chief medical officer at Family Health Centers of San Diego, one of the county’s largest providers of LGBTQ and HIV services.
The Department of Health and Human Services delayed asking the manufacturer to process the bulk vaccine the government already owned into vials.
But the federal government reportedly bungled the nation’s supply of monkeypox vaccine, leading to an unnecessary shortage. The U.S. could have had many more doses but waited too long to ask the manufacturer to process the bulk vaccine the government already owned into vials, according to the New York Times.
“Unlike HIV, a vaccine that offers protection already exists, and yet there aren’t enough vaccines to protect all of us who need it — and there could have been,” Lopez said.
The power of community trust
Max Disposti, executive director of the North County LGBTQ Resource Center, has seen a generational split in how the community has responded to monkeypox. For him and others around his age — he’s 54 — “it definitely triggers memories around AIDS, even though the response today, the stigmatizing, has been nothing compared to what we experienced in the ’80s.”

But Reynoso, who works at a nightclub with a younger staff and clientele, said the reactions he has seen to monkeypox are fear and confusion.
He said he recently got a text from someone who had tested positive and didn’t know what to do. “He was expressing enormous fear — fear of the disease and fear of the stigma. ‘How am I going to tell my employer I have to take 21 days off work to isolate? I can’t work from home.’ When you are not out with your sexuality, all of that can be an enormous problem.”
Dispelling fear and misinformation is where LGBTQ organizations like Disposti’s come in. “We are the trusted providers that can go in the community and talk to our people about prevention without stigmatizing or shaming their behavior,” he said. “Informing people reduces the panic.”
San Diego Pride and North County LGBTQ Center have been blasting information out in newsletters, social media posts and other channels.
Other groups and individuals have stepped in to share information, too, Reynoso noted. The San Diego Sisters of Perpetual Indulgence have been handing out fliers on monkeypox. A local physician, Dr. Carlton Thomas, has been posting informational videos on TikTok and Instagram.
And front and center on its website, the San Diego LGBT Community Center has a dedicated section filled with information and resources on monkeypox — referred to as hMPXV, the term for the human form of the monkeypox virus, to reduce stigma, according to Gus Hernandez, the center’s senior director of communications.
The push for education in response to monkeypox is a testament to how the LGBTQ community has grown since the AIDS epidemic, advocates agree, as they put into practice the lessons they have learned over the past 40 years to get ahead of the curve — more prepared and more powerful than ever to fight both the virus and the stigma.
Grassroots organizing helped put San Diego’s LGBTQ leadership on the political map decades ago. Now its ranks are poised to expand
Those lessons have made the LGBTQ community acutely aware of the risk they face with monkeypox, Gordon said. That has led more people in it to seek care right away, calling to ask to be vaccinated or seeking treatment after exposure.
“There’s a sense of urgency, as we’re a community who’s already lived through the HIV pandemic as well as the COVID pandemic,” Hernandez said. Many people in the community are already accustomed to frequent testing and attuned to new concerns, he added. “We know that we have to take proactive steps to protect ourselves.”
“That’s the legacy of generations of LGBTQ activists, advocates and allies who’ve worked through decades of systemic oppression, particularly in the wake of HIV/AIDS,” Lopez added.
Working together to combat the spread
The information campaign is similar to what was done during the AIDS crisis, when stigmas left those in the LGBTQ community with nowhere else to turn. “Our community has always taken care of ourselves and supported each other, because we could not trust the government was going to do the right thing,” Disposti said.
For those of us who survived the early days of the HIV/AIDS crisis, any viral infection involving our community has a triggering effect.
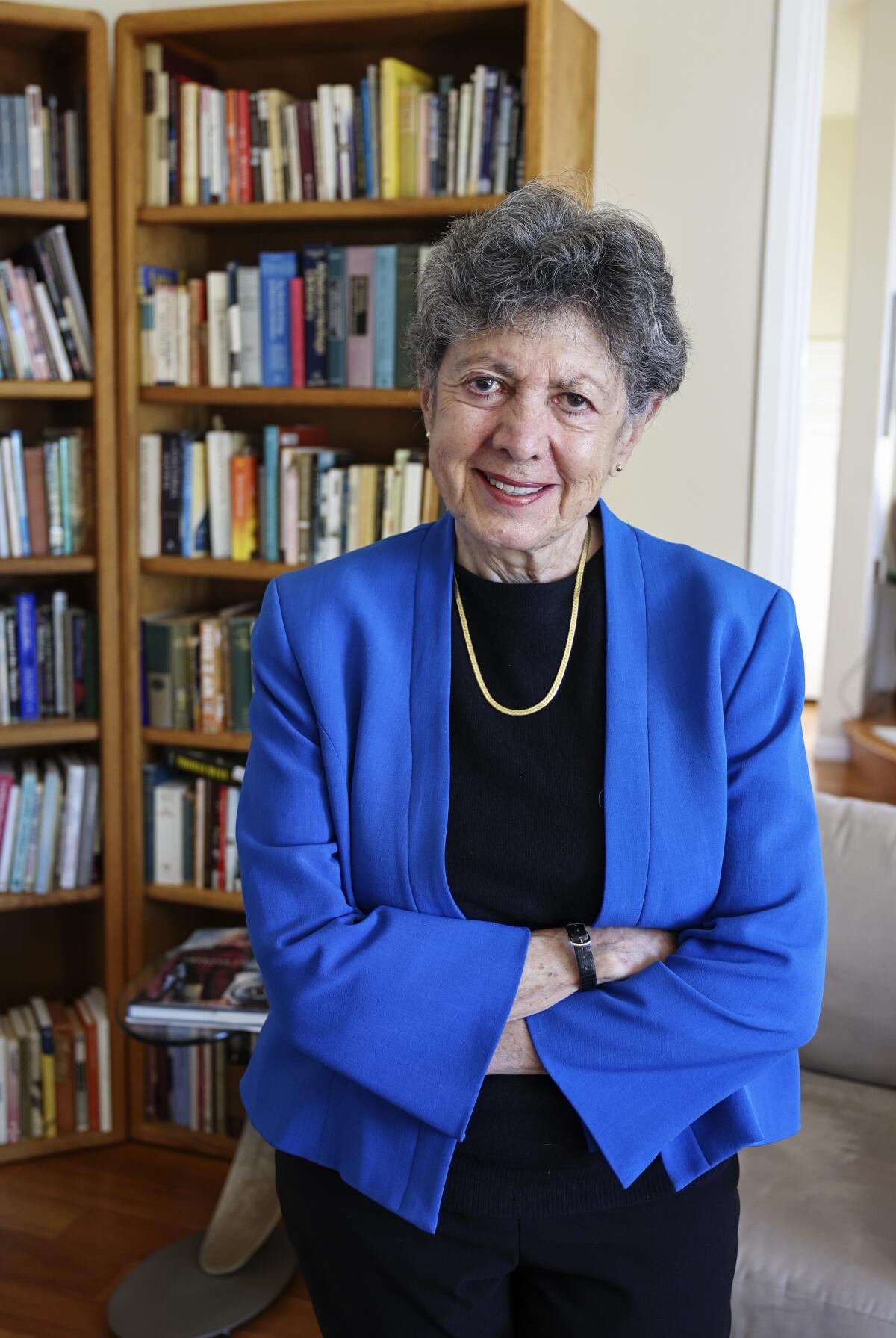
But for all the early failures on monkeypox, the current response is a far cry from what happened during the AIDS crisis, said LGBTQ historian and San Diego resident Lillian Faderman, who lost several friends to the disease in the ’80s and early ’90s.
“One thing I’ll never forget is how President Ronald Reagan wouldn’t even mention the word AIDS for many years,” she said, contrasting his approach with the current president’s. “Many lives could have been saved if [Reagan] had not only acknowledged it but put money into research and treatment.”

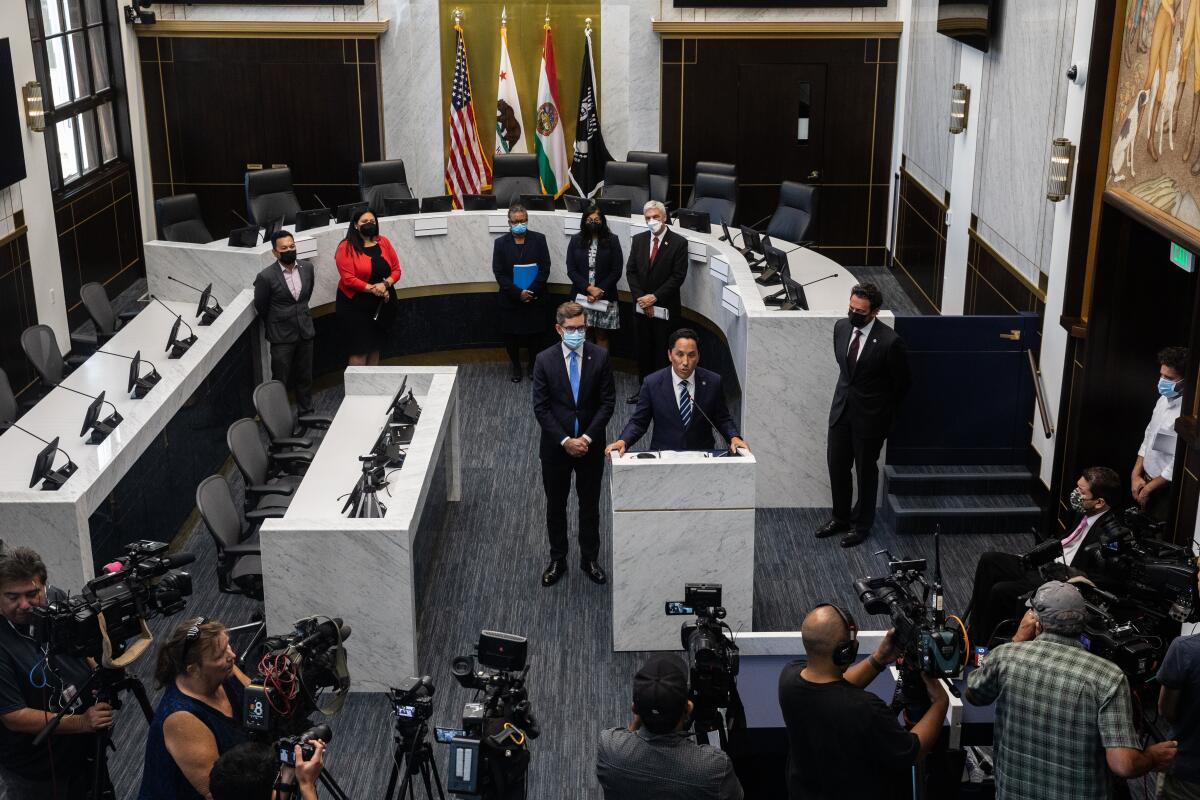
By contrast, LGBTQ leaders can now be seen working alongside public health officials in a joint effort to tackle the monkeypox virus.
When it comes to monkeypox, Lopez said it’s more important than ever to meet people with compassion, care, education and the right tools. But with vaccines, testing and treatments all in short supply, many remain frustrated that nowhere near enough is being done.
While health experts and LGBTQ leaders hope the local, state and federal emergency declarations help to expedite more doses of the much-needed vaccine, the community is focused on supporting and educating one another.
Reynoso, for instance, has seen GoFundMe pages in his social media feeds for people who have to isolate because of monkeypox and can’t work — but he says he’d like to see health officials offer hotel rooms for people who have to isolate.
And although gay men recognize they’re currently at higher risk of contracting monkeypox, health experts say that’s just where the virus is circulating right now, not necessarily where it will stay.
Smith, who is gay, is proud his community is so close-knit. “But that also allows infectious diseases to spread,” he said. “I see this over and over with lots of infectious epidemics: It hits vulnerable communities first, especially close-knit communities, and then it moves on.”
“Anytime there’s an epidemic, we’re all in it together — period,” Smith said.
To get updates about monkeypox from San Diego County, text COSD MONKEYPOX to 468-311 or call 211.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.